When you download a new app or update an old one, you’re often met with a barrage of permission requests: "Access your camera?" "Know your location?" "See your contacts?" It's easy to tap "Allow" and move on, but truly understanding and controlling App Permissions and In-App Sharing Settings is one of the most powerful ways to safeguard your digital privacy. Think of these settings as the keys to your personal data kingdom; handing them out indiscriminately can open the door to unwanted snooping, data breaches, and even identity theft.
This isn't about fear-mongering; it's about empowerment. We're going to dive deep into what these permissions mean, why they matter, and crucially, how you can manage them effectively across your devices. By the end, you'll be a digital guardian, confidently navigating your settings with purpose and precision.
At a Glance: Your Digital Privacy Toolkit
- Permissions are Access Passes: They determine what parts of your device and data an app can touch.
- Default Settings Aren't Always Best: Most apps ask for more access than they truly need.
- Context is Key: A camera app needs camera access; a calculator app absolutely does not.
- "Allow Only While Using" is Your Friend: Especially for location and microphone.
- In-App Sharing Settings Go Deeper: Beyond system permissions, apps often have their own internal settings for sharing your data with third parties.
- Regular Reviews are Essential: Your privacy posture isn't a one-time setup; it needs ongoing attention.
- You're in Control: Learning to manage these settings puts you back in the driver's seat of your digital life.
The Silent Agreement: What Are App Permissions Anyway?
Every time you install an app, whether on your smartphone, tablet, or PC, you're entering into a silent agreement. That agreement is governed by permissions. Fundamentally, app permissions are explicit requests from an application to access specific features or data on your device. This could be anything from your camera and microphone to your photo gallery, contacts list, or precise location.
Operating systems like Android and Windows have built-in security frameworks that mediate these requests. They don't just let an app do whatever it wants; they require the app to ask you, the user, for permission first. The challenge lies in the fact that these requests can often be vague, numerous, or simply ignored in the rush to start using the app.
Why Do Apps Ask for So Much? (And When Is It Too Much?)
From an app developer's perspective, asking for permissions makes sense. A video conferencing app needs access to your camera and microphone. A maps app needs your location. A photo editor needs access to your files and media. These are legitimate, functional requirements.
The problem arises when apps ask for permissions that are completely unrelated to their core function. Why would a simple flashlight app need access to your contacts or call history? Why does a casual game need your precise location "all the time"? This over-permissioning can be driven by several factors:
- Feature Creep: Developers add more features over time, each potentially requiring new permissions.
- Ad Tracking: Many free apps rely on advertising, and advertisers often demand extensive data collection (including location, contacts, and activity) for targeted ads.
- Data Monetization: Some apps, particularly those that are "free," may collect and sell user data to third-party data brokers.
- Laziness/Poor Design: Sometimes, developers just request a broad set of permissions without refining them, making it easier for them but riskier for you.
The "too much" threshold is crossed when an app requests access to data or features that have no logical connection to its advertised purpose. This is where your critical thinking becomes your best defense.
The Privacy Cost of Unchecked Access
Granting unnecessary permissions isn't just a minor inconvenience; it carries tangible risks to your privacy and security.
- Location Tracking: An app with "Always Allow" location access can build a detailed profile of where you go, even when you're not actively using the app. This data can be sold, used for targeted advertising, or potentially even exploited in more malicious ways.
- Unauthorized Recordings: Giving camera or microphone access to a rogue app could allow it to record you or your conversations without your knowledge, transmitting that data to a third party.
- Contact Harvesting: An app with contacts access could upload your entire address book to its servers, using that data for spam, phishing attacks, or expanding its own network without your contacts' consent.
- Data Breaches: If an app you've granted extensive permissions to suffers a data breach, all the personal data it collected from your device could be exposed.
The goal isn't to deny every permission to every app. It's to be intentional and informed about what you're sharing.
Decoding Android Permissions: Your Mobile Control Center
Android's permission system has evolved significantly, offering granular control over your data. Understanding these categories is the first step to becoming a privacy pro.
Key Android Permission Categories Explained
Each permission category covers a range of sensitive data or device capabilities. Here's a breakdown of the most common ones and why you should care:
- Body Sensors: Accesses sensitive health data like heart rate, oxygen levels, or step counts.
- Why it matters: Primarily used by fitness and health tracking apps. Grant carefully, as this data is highly personal.
- Calendar: Allows apps to read, create, and modify events.
- Why it matters: Granting to untrusted apps can expose your schedule, appointments, and potentially location data.
- Call History: Lets apps see and change your call logs.
- Why it matters: Mostly for dialer apps. Limit access due to the sensitive nature of your communication records.
- Camera: Grants access to your phone's front and rear cameras.
- Why it matters: Essential for photography, QR code scanners, and video calls. Misuse can lead to unauthorized recordings of you or your surroundings.
- Contacts: Allows apps to read, edit, or sync your phone book.
- Why it matters: Grant extremely carefully. Exploitation can lead to your contacts being used for spam, phishing, or even identity theft by third parties.
- Files and Media: Enables access to modify or read files stored on your device's internal storage or SD card.
- Why it matters: Crucial for file managers, cloud storage, or photo editors. Vet apps carefully to prevent unauthorized access or deletion of your personal files.
- Health Connect: Links apps to Google’s Health Connect, a centralized platform for sharing health and fitness data between different apps.
- Why it matters: Provides a single hub for health data. Only grant access to trusted health and fitness apps you actively use.
- Location: Apps may request precise (GPS, network) or approximate (Wi-Fi, cellular) location.
- Why it matters: Essential for navigation, ride-sharing, or weather apps. Unnecessary access (especially "All the time") is a major privacy compromise. If you're wondering why your location won't share in a specific app, checking its permissions is often the first step.
- Microphone: Enables voice input, recording, and interaction.
- Why it matters: Required for voice assistants, recording apps, and video calls. Malware can misuse this for eavesdropping on your private conversations.
- Nearby Devices: Connects to Bluetooth, Wi-Fi Direct, or other nearby devices.
- Why it matters: Needed for smart devices or casting. Be cautious to prevent unwanted pairing or data sharing with unknown devices.
- Notifications: Allows apps to send push notifications.
- Why it matters: While not directly data access, excessive or spammy notifications can be disruptive and hint at aggressive marketing tactics.
- Phone: Enables apps to make/manage calls and access your phone number.
- Why it matters: Grant only if directly tied to the app's core function (e.g., a custom dialer) to prevent unauthorized calls or number harvesting.
- Photos and Videos: Grants access to or allows editing of your media library.
- Why it matters: Be selective to prevent personal photos or videos from being misused, uploaded, or shared without your explicit consent.
- SMS: Allows apps to read, send, or delete text messages.
- Why it matters: Useful for messaging apps or OTP auto-fill features. Misuse can lead to serious security breaches, unauthorized charges, or spamming your contacts.
How to Manage Android App Permissions (Step-by-Step)
Android offers two main ways to manage permissions: by app or by permission type.
Method 1: Changing Permissions for a Specific App
This is ideal when you're reviewing a single app you've just installed or suspect might be misbehaving.
- Open your phone's Settings app. You can usually find this by swiping down from the top of your screen and tapping the gear icon, or by finding the "Settings" app icon in your app drawer.
- Tap on Apps (or "Apps & notifications," "App management," depending on your Android version).
- You'll likely see a list of recently opened apps. To find the one you want, tap See all apps (or "Manage apps").
- Scroll through the list and tap the desired app.
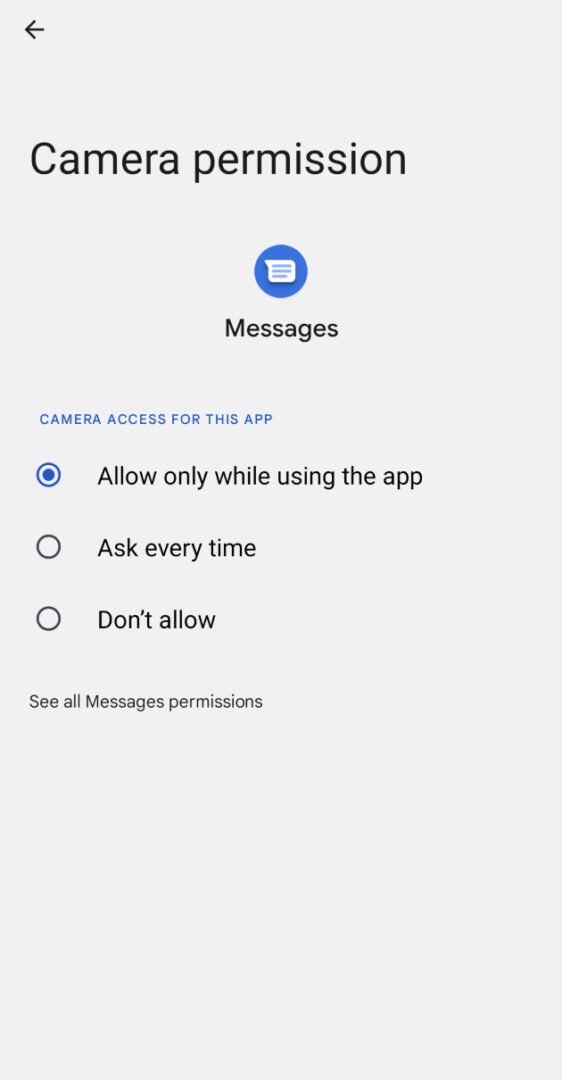
- On the app's info page, tap Permissions. This will show you all the permissions the app has requested and which ones it currently has access to.
- Tap a specific permission you want to review (e.g., Location, Camera, Contacts).
- Choose one of the available options:
- Allow: Grants full access. Use sparingly.
- Don’t allow: Denies access. The app might not function correctly without it.
- Ask every time: Prompts you for approval each time the app tries to use that permission. Excellent for sensitive permissions like microphone or camera.
- Allow only while using the app: Access is granted only when the app is actively open on your screen. This is often the best choice for location, camera, and microphone.
- All the time (for Location only): Allows the app to access your location even when it's not in use. Rarely necessary, and a significant privacy risk.
Method 2: Managing Permissions by Type (The Permissions Manager)
This method is great for a periodic privacy audit, allowing you to see which apps have access to a particular sensitive data point, like your contacts or location.
- Open your phone's Settings app.
- Navigate to Security and Privacy (or "Privacy," "Privacy & Security," depending on your Android version).
- Under the "Privacy" section, tap Permissions Manager.
- You'll see a list of all permission categories (e.g., Camera, Contacts, Location) and the number of apps that currently have access to each.
- Tap a permission category (e.g., Location) to see a list of all apps that have requested that specific permission.
- For each app listed, you'll see its current access status ("Allowed all the time," "Allowed only while in use," "Denied"). Tap on an app to modify its access rights using the same options described in Method 1.
Actionable Insights for Android Users
- Review Regularly: Make it a habit to check app permissions once a month or every time you install a new app.
- Question Everything: If an app's permission request doesn't align with its core function, deny it or choose "Ask every time."
- Limit "All the Time" Access: Especially for location. Very few apps genuinely need constant background location access.
- Battery Life Boost: Denying unnecessary background permissions can actually help save battery life, as apps won't constantly be performing tasks like location checks.
- Data Control: This customization empowers you to truly control what data leaves your device.
Navigating Windows 11 App Permissions: Desktop Control
Your Windows 11 PC also has a robust permission system, controlling what desktop apps and Microsoft Store apps can access. Managing these is crucial for maintaining privacy on your computer.
Steps to Change App Permissions in Windows 11
- Open Settings: Click the Start button (Windows logo) on your taskbar and select the Settings gear icon. Alternatively, press
Windows key + I. - Access Privacy & Security: In the left-hand navigation pane of the Settings window, click on Privacy & security.
- Select App Permissions: Scroll down to the "App permissions" section on the right side. Here, you'll see a list of permission categories.
- Choose a Permission Category: Click on a specific category (e.g., Camera, Microphone, Location) to view which apps have requested access.
- Toggle Permissions:
- At the top of each category page, you'll usually see a master toggle (e.g., "Camera access"). Turning this off will disable camera access for all apps on your system.
- Below the master toggle, you'll find a list of individual apps. Toggle the switch next to each app to enable or disable its permission for that specific category.
Actionable Insights for Windows 11 Users
- Routine Checks: Just like on mobile, regularly review your Windows 11 app permissions, especially after installing new software or major system updates.
- Developer Trust: Be extra cautious when granting permissions to apps downloaded from outside the Microsoft Store or from unknown developers.
- Least Privilege: Grant only the permissions absolutely necessary for an app to function. If an app works without a certain permission, keep it off.
- Purpose Before Granting: Always consider why an app needs a particular permission. Does your PDF viewer really need microphone access? Probably not.
- Reset Options: If you feel overwhelmed or have made too many changes, some categories in "Privacy & security" (like "General" privacy settings) offer a "Reset" button to restore default settings. Note that app-specific permission changes often need to be reverted manually.
- Malfunction vs. Privacy: If an app stops working after you deny a permission, you can easily go back and re-enable it. Apps generally don't notify you of permission changes.
Beyond System Controls: In-App Sharing Settings
While system-level permissions dictate what an app can access on your device, in-app sharing settings control how the app itself uses and shares the data it collects internally. This is a critical distinction often overlooked.
Imagine you've given a social media app permission to access your photos (system permission). Within that app, there will be settings about who can see your posts, who can tag you, whether your posts are shared with "friends of friends," or if your data is used for personalized ads or shared with third-party partners. These are in-app sharing settings.
Why In-App Sharing Settings Matter
- Third-Party Data Sharing: Many apps, especially free ones, partner with data brokers, advertisers, or analytics companies. Your in-app settings often let you limit (or opt-out of) this sharing.
- Personalization vs. Privacy: Apps use your data to "personalize" your experience. While some personalization is helpful, it can come at the cost of broad data collection.
- Social Graph Exploitation: Social apps can leverage your connections to grow their network, sometimes without your explicit consent (e.g., suggesting you connect with people you've only emailed once).
- Ad Targeting: Beyond what system permissions allow for ad tracking, in-app settings often provide granular control over the types of ads you see and whether your data is used for that purpose.
How to Find and Manage In-App Sharing Settings (General Guidance)
Unlike system permissions, there's no universal "In-App Sharing Settings Manager." These settings are unique to each application and usually found within the app itself.
- Open the App: Launch the app you want to review.
- Look for Settings/Privacy/Account: Navigate to the app's internal settings. This is often represented by a gear icon, three horizontal lines (hamburger menu), or found under your profile/account section.
- Find Privacy, Data, or Sharing Sections: Within the app's settings, look for sections explicitly named "Privacy," "Data & Privacy," "Sharing," "Account Settings," "Ads," or "Third-Party Access."
- Review and Adjust:
- Data Sharing: Look for toggles or options related to sharing your data with "third-party partners," "advertisers," or "analytics providers." Turn these off if you want to limit sharing.
- Personalized Ads: Opt-out of personalized or targeted advertising if available.
- Content Visibility: For social apps, define who can see your posts, photos, and personal information.
- Location History: Some apps keep their own detailed location history, separate from system permissions. Look for options to clear or disable this.
- Connected Accounts: Review any external accounts (like Google, Facebook, Apple) you've used to sign into the app, and adjust what data is shared between them.
This process requires a bit more legwork, but it's crucial for a complete privacy strategy. Make it a point to do this for your most used and most data-hungry apps (social media, messaging, shopping, health apps).
Best Practices for Digital Guardianship
Becoming proficient in managing app permissions and in-app sharing settings is an ongoing journey. Here are some overarching principles to guide you:
- The Principle of Least Privilege: Grant apps only the absolute minimum permissions they need to function. If a feature isn't essential to you, don't grant the permission that enables it.
- Read (Selected Parts of) Privacy Policies: While entire privacy policies are often dense, quickly skim for sections on "data sharing," "third parties," and "data retention." This can reveal a lot about an app's practices.
- Think Before You Tap: That initial permission request is your best opportunity to make an informed decision. Don't mindlessly click "Allow."
- Regular Privacy Audits: Schedule quarterly "privacy check-ups" for yourself. Go through your app permissions on your phone and PC, and review in-app settings for your most-used apps.
- Consider Paid Alternatives: If a "free" app seems overly intrusive, consider if a paid alternative that doesn't rely on data monetization might be worth the investment.
- Keep Software Updated: Operating system updates often include enhanced privacy controls and security patches. Keep your Android, iOS, and Windows devices up to date.
- Uninstall Unused Apps: Less apps mean fewer potential data collectors. If you haven't used an app in months, delete it.
Common Questions & Misconceptions
Will denying a permission break the app?
Sometimes, yes. If you deny a core permission (e.g., Camera access for a camera app), the app may crash or refuse to open that specific feature. However, many apps will simply degrade gracefully, offering a warning that a feature won't work without permission. It's often worth trying to deny first to see if the app still meets your needs.
Do apps know when I change permissions?
Generally, no. Operating systems typically don't send a notification to the app when you revoke its permissions. The app will only discover it when it tries to access the denied resource and the OS blocks it.
Is "Allow only while using" always best?
For sensitive permissions like Location, Microphone, and Camera, "Allow only while using the app" (or "Ask every time") is often the best balance between functionality and privacy. It grants the app what it needs when you're actively interacting with it, but stops background access.
What about system apps? Can I control their permissions?
Yes, for many system apps, you can manage permissions just like third-party apps. However, some core system services might have essential permissions that cannot be revoked without impacting basic device functionality. Exercise caution and research before revoking permissions for critical system apps.
Are all permissions equally risky?
No. Permissions that grant access to your location, contacts, camera, microphone, SMS, and files are generally considered the most sensitive due to the highly personal nature of the data involved. Others, like notification access, pose less direct privacy risk but can still impact your experience.
Your Data, Your Rules: Taking Control
In our increasingly connected world, data privacy isn't a luxury; it's a fundamental right. Understanding and actively managing app permissions and in-app sharing settings isn't just about protecting yourself from malicious actors; it's about reclaiming agency over your digital identity.
By making conscious choices about what you share, when you share it, and with whom, you transform from a passive consumer into an active participant in your digital life. Start today by reviewing the permissions of your most-used apps. You'll be surprised at what you find, and empowered by the control you regain.